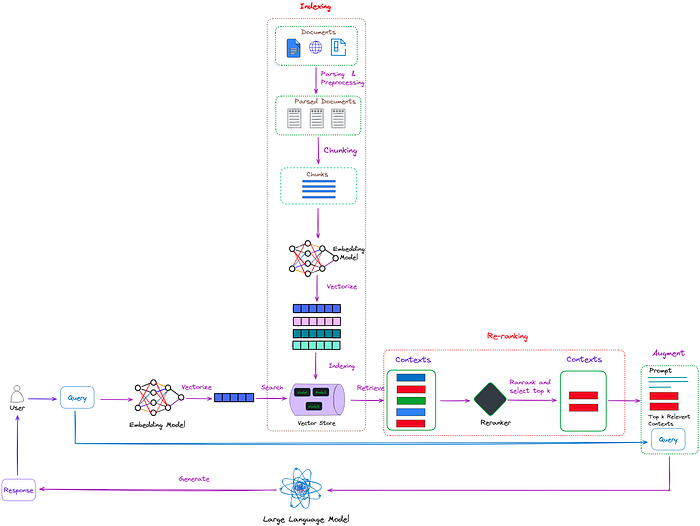
Re-ranking在检索增广生成(RAG)过程中起着至关重要的作用。在朴素的RAG方法中,可以检索大量上下文,但并非所有上下文都与问题相关。重新排序允许对文档进行重新排序和过滤,将相关的文档放在最前面,从而提高RAG的有效性。
本文介绍了RAG的重新排序技术,并演示了如何使用两种方法合并重新排序功能
介绍Re-ranking
图1:在RAG中重排,重排的任务是评估这些上下文的相关性,并优先考虑最有可能提供准确和相关答案的上下文(红框)。图片来自作者。
如图1所示,重排的任务就像一个智能过滤器。当检索器从索引集合中检索多个上下文时,这些上下文可能与用户的查询具有不同的相关性。有些上下文可能非常相关(在图1中的红色框中突出显示),而其他上下文可能只是稍微相关,甚至不相关(在图1中的绿色和蓝色框中突出显示)。
重排的任务是评估这些上下文的相关性,并优先考虑最有可能提供准确和相关答案的上下文。这允许LLM在生成答案时优先考虑这些排名靠前的上下文,从而提高响应的准确性和质量。
简单来说,重新排名就像在开卷考试中帮助你从一堆学习材料中选择最相关的参考资料 ,这样你就可以更有效、更准确地回答问题。
本文介绍的重新排序方法主要分为以下两种:
重新排序模型:这些模型考虑文档和查询之间的交互特征,以更准确地评估它们的相关性。
LLM:LLM的出现为重新排名开辟了新的可能性。通过彻底理解整个文档和查询,可以更全面地捕获语义信息。
使用Rerank模型 与Embedding模型不同,重排序模型以查询和上下文作为输入,直接输出相似度分数,而不是Embeddings。重要的是要注意,重新排序模型是使用交叉熵损失函数 进行优化的,允许不限于特定范围的相关性分数,甚至可以是负的。
目前,没有很多可用的重排模型。一种选择是Cohere 提供的在线模型,可以通过API访问。还有一些开源模型,如big-reranker-base和big-reranker-large 等。
图2显示了使用命中率和平均倒数排名(MRR)指标的评估结果:
图2:使用命中率和平均倒数排名(MRR)指标的评估结果。来源:提升RAG:选择最佳Embedding和重新排名模型
从这个评价结果,我们可以看到:
无论使用何种Embedding模型,重排都具有更高的命中率和MRR,表明重新排名的影响显著。 目前,最好的重新排名模式是Cohere ,但它是一个付费服务。开源big-rerrank-large 模型具有与cohere类似的功能。
在本文中,将使用基于更大rank的模型。
环境配置 导入相关库,设置环境变量和全局变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import osos.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY" ] = "YOUR_OPENAI_KEY" from llama_index import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReaderfrom llama_index.postprocessor.flag_embedding_reranker import FlagEmbeddingRerankerfrom llama_index.schema import QueryBundledir_path = "YOUR_DIR_PATH"
目录中只有一个PDF文件,使用的是论文“TinyLlama:一个开源的小型语言模型 ”。
1 2 (py) Florian:~ Florian$ ls /Users/Florian/Downloads/pdf_test/ tinyllama.pdf
使用LlamaIndex构建一个简单的检索器 1 2 3 documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(dir_path).load_data() index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents) retriever = index.as_retriever(similarity_top_k = 3 )
基本检索 1 2 3 4 5 query = "Can you provide a concise description of the TinyLlama model?" nodes = retriever.retrieve(query) for node in nodes: print ('----------------------------------------------------' ) display_source_node(node, source_length = 500 )
display_source_node函数改编自llama_index源代码 。原来的功能是为Jupyter notebook设计的,所以做了如下修改:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 from llama_index.schema import ImageNode, MetadataMode, NodeWithScorefrom llama_index.utils import truncate_textdef display_source_node ( source_node: NodeWithScore, source_length: int = 100 , show_source_metadata: bool = False , metadata_mode: MetadataMode = MetadataMode.NONE, None : """Display source node""" source_text_fmt = truncate_text( source_node.node.get_content(metadata_mode=metadata_mode).strip(), source_length ) text_md = ( f"Node ID: {source_node.node.node_id} \n" f"Score: {source_node.score} \n" f"Text: {source_text_fmt} \n" ) if show_source_metadata: text_md += f"Metadata: {source_node.node.metadata} \n" if isinstance (source_node.node, ImageNode): text_md += "Image:" print (text_md)
基本检索结果如下,表示重排前的前3个节点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: 438b9d91-cd5a-44a8-939e-3ecd77648662 Score: 0.8706055408845863 Text: 4 Conclusion In this paper, we introduce TinyLlama, an open-source, small-scale language model. To promote transparency in the open-source LLM pre-training community, we have released all relevant infor- mation, including our pre-training code, all intermediate model checkpoints, and the details of our data processing steps. With its compact architecture and promising performance, TinyLlama can enable end-user applications on mobile devices, and serve as a lightweight platform for testing a w... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: ca4db90f-5c6e-47d5-a544-05a9a1d09bc6 Score: 0.8624531691777889 Text: TinyLlama: An Open-Source Small Language Model Peiyuan Zhang∗Guangtao Zeng∗Tianduo Wang Wei Lu StatNLP Research Group Singapore University of Technology and Design {peiyuan_zhang , tianduo_wang , @sutd.edu.sg">luwei }@sutd.edu.sg guangtao_zeng@mymail.sutd.edu.sg Abstract We present TinyLlama, a compact 1. 1B language model pretrained on around 1 trillion tokens for approximately 3 epochs. Building on the architecture and tok- enizer of Llama 2 (Touvron et al., 2023b), TinyLlama leverages various advances contr... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: e2d97411-8dc0-40a3-9539-a860d1741d4f Score: 0.8346160605298356 Text: Although these works show a clear preference on large models, the potential of training smaller models with larger dataset remains under-explored. Instead of training compute-optimal language models, Touvron et al. (2023a) highlight the importance of the inference budget, instead of focusing solely on training compute-optimal language models. Inference-optimal language models aim for optimal performance within specific inference constraints This is achieved by training models with more tokens...
Re-ranking 要对上述节点重排,请使用基于bge-reranker-base模型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 print ('------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------' )print ('Start reranking...' )reranker = FlagEmbeddingReranker( top_n = 3 , model = "BAAI/bge-reranker-base" , ) query_bundle = QueryBundle(query_str=query) ranked_nodes = reranker._postprocess_nodes(nodes, query_bundle = query_bundle) for ranked_node in ranked_nodes: print ('----------------------------------------------------' ) display_source_node(ranked_node, source_length = 500 )
重排后的结果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Start reranking... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: ca4db90f-5c6e-47d5-a544-05a9a1d09bc6 Score: -1.584416151046753 Text: TinyLlama: An Open-Source Small Language Model Peiyuan Zhang∗Guangtao Zeng∗Tianduo Wang Wei Lu StatNLP Research Group Singapore University of Technology and Design {peiyuan_zhang , tianduo_wang , @sutd.edu.sg">luwei }@sutd.edu.sg guangtao_zeng@mymail.sutd.edu.sg Abstract We present TinyLlama, a compact 1. 1B language model pretrained on around 1 trillion tokens for approximately 3 epochs. Building on the architecture and tok- enizer of Llama 2 (Touvron et al., 2023b), TinyLlama leverages various advances contr... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: e2d97411-8dc0-40a3-9539-a860d1741d4f Score: -1.7028117179870605 Text: Although these works show a clear preference on large models, the potential of training smaller models with larger dataset remains under-explored. Instead of training compute-optimal language models, Touvron et al. (2023a) highlight the importance of the inference budget, instead of focusing solely on training compute-optimal language models. Inference-optimal language models aim for optimal performance within specific inference constraints This is achieved by training models with more tokens... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: 438b9d91-cd5a-44a8-939e-3ecd77648662 Score: -2.904750347137451 Text: 4 Conclusion In this paper, we introduce TinyLlama, an open-source, small-scale language model. To promote transparency in the open-source LLM pre-training community, we have released all relevant infor- mation, including our pre-training code, all intermediate model checkpoints, and the details of our data processing steps. With its compact architecture and promising performance, TinyLlama can enable end-user applications on mobile devices, and serve as a lightweight platform for testing a w...
可以看出,重新排序后,ID为ca4db90f-5c6e-47d5-a544-05a9a1d09bc6的节点的排序由2变为1。这意味着最相关的上下文被排在第一位。
使用LLM作为ranker 现有涉及LLM的重排序方法大致可以分为三类:带重排任务的微调LLM 、使用提示工程的LLM重排 ,以及在训练过程中使用LLM进行数据增强 。
使用提示工程的LLM重排 方法成本较低。下面是使用RankGPT 的演示,它已集成到LlamaIndex 中。
RankGPT 的思想是使用LLM(如ChatGPT或GPT-4或其他大语言模型)执行zero-shot顺序通道重新排名。它采用排列生成方法和滑动窗口策略来有效地重新排列通道。
如图3所示,论文 提出了三种可行的方法。
图3:使用大语言模型对zero-shot通道重新排序的三种指令。灰色和黄色块表示模型的输入和输出。(a)查询生成依赖于大语言模型的日志概率来生成基于段落的查询。(b)关联生成指导大语言模型输出关联判断。(c)置换生成生成一组段落的排序列表。来源:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.09542.pdf
前两种方法是传统的方法,其中给每个文档一个分数,然后根据这个分数对所有段落进行排序。
本文提出了第三种方法——置换生成法。具体来说,该模型不依赖于外部评分,而是直接对段落进行端到端排序。 也就是说,直接利用LLM的语义理解能力,对所有候选段落进行相关度排序。
然而,通常候选文档的数量非常大,而LLM的输入是有限的。因此,一次输入所有文本通常是不可能的。
图4:使用窗口大小为4、步长为2的滑动窗口对8个通道重新排序的示意图。蓝色表示前两个窗口,而黄色表示最后一个窗口。滑动窗口以“从后到先”的顺序应用,这意味着前一个窗口中的前两个段落将参与下一个窗口的重新排序。来源:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.09542.pdf
因此,如图4所示,引入了一种滑动窗口方法,它遵循冒泡排序的思想。每次只对第一个**4** 文本进行排序,然后移动窗口,对随后的**4** 文本进行排序。通过对整个文本进行迭代,我们可以得到性能最好的top文本。
请注意,为了使用RankGPT,您需要安装较新版本的LlamaIndex。我之前安装的版本(0.9.29)不包括RankGPT所需的代码。因此,我使用LlamaIndex版本0.9.45.post1创建了一个新的conda环境。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from llama_index.postprocessor import RankGPTRerankfrom llama_index.llms import OpenAIreranker = RankGPTRerank( top_n = 3 , llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-16k" ), )
总体结果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 (llamaindex_new) Florian:~ Florian$ python /Users/Florian/Documents/rerank.py ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: 20de8234-a668-442d-8495-d39b156b44bb Score: 0.8703492815379594 Text: 4 Conclusion In this paper, we introduce TinyLlama, an open-source, small-scale language model. To promote transparency in the open-source LLM pre-training community, we have released all relevant infor- mation, including our pre-training code, all intermediate model checkpoints, and the details of our data processing steps. With its compact architecture and promising performance, TinyLlama can enable end-user applications on mobile devices, and serve as a lightweight platform for testing a w... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: 47ba3955-c6f8-4f28-a3db-f3222b3a09cd Score: 0.8621633467539512 Text: TinyLlama: An Open-Source Small Language Model Peiyuan Zhang∗Guangtao Zeng∗Tianduo Wang Wei Lu StatNLP Research Group Singapore University of Technology and Design {peiyuan_zhang , tianduo_wang , @sutd.edu.sg">luwei }@sutd.edu.sg guangtao_zeng@mymail.sutd.edu.sg Abstract We present TinyLlama, a compact 1. 1B language model pretrained on around 1 trillion tokens for approximately 3 epochs. Building on the architecture and tok- enizer of Llama 2 (Touvron et al., 2023b), TinyLlama leverages various advances contr... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: 17cd9896-473c-47e0-8419-16b4ac615a59 Score: 0.8343984516104476 Text: Although these works show a clear preference on large models, the potential of training smaller models with larger dataset remains under-explored. Instead of training compute-optimal language models, Touvron et al. (2023a) highlight the importance of the inference budget, instead of focusing solely on training compute-optimal language models. Inference-optimal language models aim for optimal performance within specific inference constraints This is achieved by training models with more tokens... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Start reranking... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: 47ba3955-c6f8-4f28-a3db-f3222b3a09cd Score: 0.8621633467539512 Text: TinyLlama: An Open-Source Small Language Model Peiyuan Zhang∗Guangtao Zeng∗Tianduo Wang Wei Lu StatNLP Research Group Singapore University of Technology and Design {peiyuan_zhang , tianduo_wang , @sutd.edu.sg">luwei }@sutd.edu.sg guangtao_zeng@mymail.sutd.edu.sg Abstract We present TinyLlama, a compact 1. 1B language model pretrained on around 1 trillion tokens for approximately 3 epochs. Building on the architecture and tok- enizer of Llama 2 (Touvron et al., 2023b), TinyLlama leverages various advances contr... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: 17cd9896-473c-47e0-8419-16b4ac615a59 Score: 0.8343984516104476 Text: Although these works show a clear preference on large models, the potential of training smaller models with larger dataset remains under-explored. Instead of training compute-optimal language models, Touvron et al. (2023a) highlight the importance of the inference budget, instead of focusing solely on training compute-optimal language models. Inference-optimal language models aim for optimal performance within specific inference constraints This is achieved by training models with more tokens... ---------------------------------------------------- Node ID: 20de8234-a668-442d-8495-d39b156b44bb Score: 0.8703492815379594 Text: 4 Conclusion In this paper, we introduce TinyLlama, an open-source, small-scale language model. To promote transparency in the open-source LLM pre-training community, we have released all relevant infor- mation, including our pre-training code, all intermediate model checkpoints, and the details of our data processing steps. With its compact architecture and promising performance, TinyLlama can enable end-user applications on mobile devices, and serve as a lightweight platform for testing a w...
请注意,由于使用LLM,重新排名后的分数没有更新 。当然,这不是至关重要的。
从结果中可以看出,重新排序后,排名前1的结果是包含答案的正确文本,这与之前使用重新排序模型得到的结果一致。
评估 我们可以修改第三节的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 reranker = FlagEmbeddingReranker( top_n = 3 , model = "BAAI/bge-reranker-base" , use_fp16 = False ) query_engine = index.as_query_engine( similarity_top_k = 3 , node_postprocessors=[reranker] )
感兴趣的读者可以试用一下。
结论 总体而言,本文介绍了重新排序的原理和两种主流方法。
其中,使用重排序模型的方法是轻量级的,开销较小。
另一方面,使用LLM的方法在多个基准测试中表现良好 但成本较高,并且仅在使用ChatGPT和GPT-4时表现良好,而在使用FLAN-T5和Vicuna-13B等其他开源模型时表现不佳。
因此,在实际项目中,需要进行特定的权衡。
英文原文:https://pub.towardsai.net/advanced-rag-04-re-ranking-85f6ae8170b1